Semi-Conductor Industry
Our capacitive tapes deliver precise, reliable, high-temperature resistant solutions across electronics, automotive, and high-precision industries.
- Home
- Semi-Conductor Industry
Semiconductor Industry
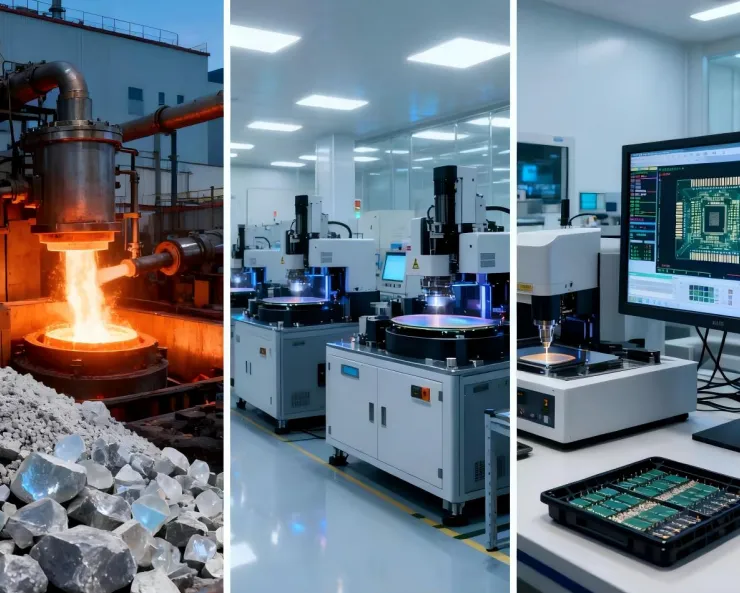
The semiconductor industry encompasses R&D, manufacturing, packaging, testing, and related equipment/software, focusing on producing key components like chips using controllable semiconductor materials (e.g., silicon, germanium).
Key Benefits
- Industrial Chain : Covers upstream materials and equipment, midstream wafer production and testing, and downstream applications in electronics, automotive, and communications.
- Strategic Significance : As the foundation of the electronic information industry, it drives AI, IoT, and new energy vehicle development, supporting technological progress and economic growth.



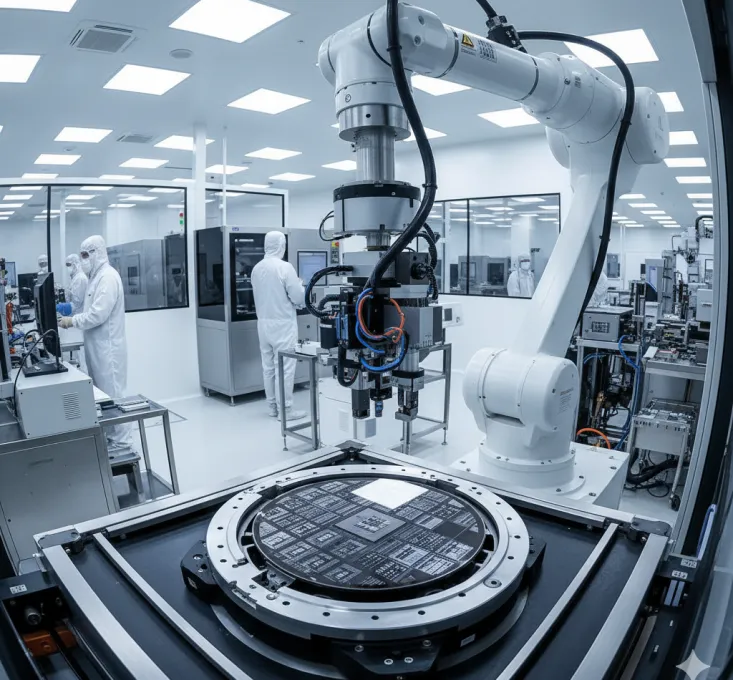
How it Works
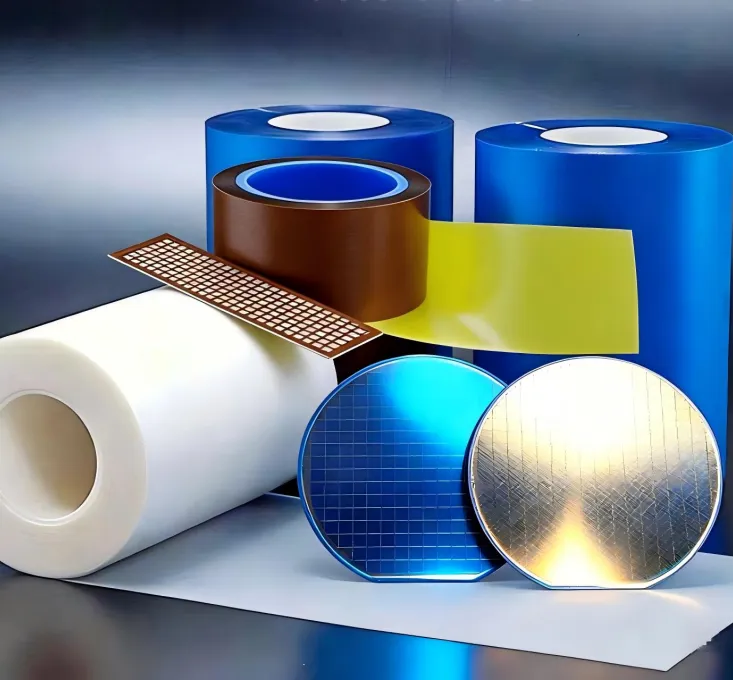
High-temperature tape is essential in the semiconductor industry, providing protection, insulation, masking, and stability to ensure process safety and precision.
Component
Shields semiconductor components from damage during packaging, soldering, and reflow processes.
Circuit Insulation
Isolates circuits to prevent short circuits and electrical interference.
Precision Masking & Positioning
Enables accurate masking and positioning in coating, etching, and other processes.
Durability
Resists chemicals and abrasion, ensuring stable and reliable handling throughout manufacturing.
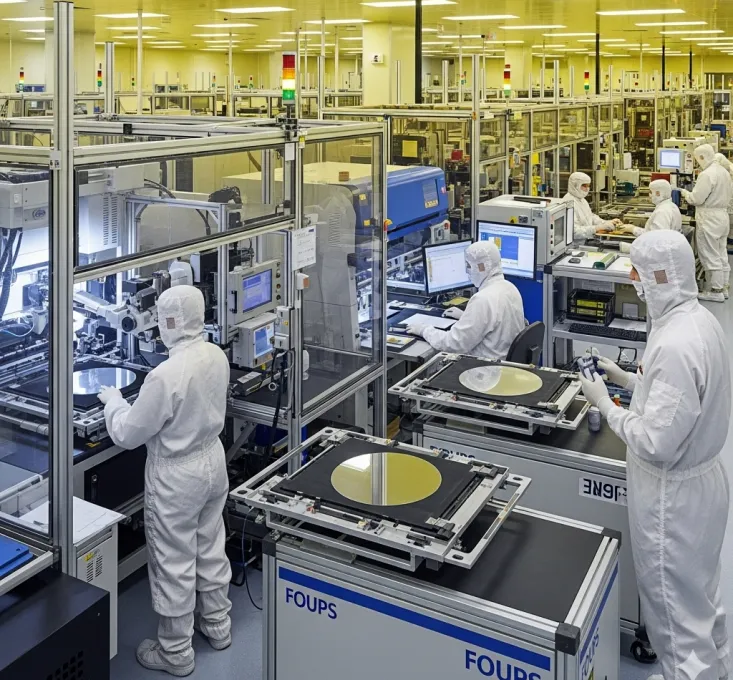
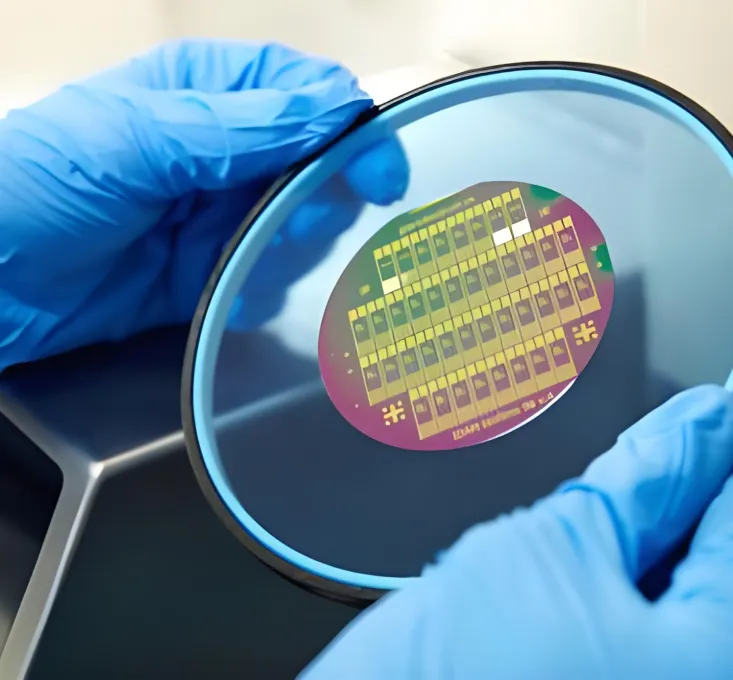



Core Element for
Innovation & Excellence
Ensuring Process Safety
The insulating function prevents short circuits, electrical interference, and device damage.
Maintaining Electrical Performance
The insulating function prevents short circuits, electrical interference, and device damage.
Improving Production Efficiency
Stable fixation and chemical resistance reduce process defects and rework, minimizing production losses.
Core Significance
High-temperature tape is an indispensable auxiliary material in semiconductor manufacturing, ensuring component safety, process accuracy, and production efficiency.
Comprehensive Solution
Polyimide tape can withstand high temperatures above 250°C, making it suitable for high-temperature processes such as reflow soldering, curing, and baking. It protects wafers, chips, and sensitive components from heat damage. Polyimide itself is an insulating material with high dielectric strength, preventing short circuits, electrical interference, and electrostatic damage, thereby ensuring the safety of circuits and chips. It also has high resistance to chemicals such as acids, bases, and solvents. During processes like etching, cleaning, and vapor deposition, it can mask and protect sensitive areas, preventing corrosion or contamination. Select 9 more words to run Humanizer.
PET tape can be used to protect the surfaces of wafers and chips. During handling, cutting, and packaging, PET tape covers sensitive areas to prevent scratches, contamination, and electrostatic damage. In automated production lines or testing processes, it is used to secure wafers, chips, or other tiny components, improving processing accuracy and production efficiency. It can also be used for the transportation and packaging of wafers or components, providing mechanical cushioning and surface protection.
Anti-static polyimide tape combines high-temperature resistance, insulation, and anti-static properties to protect sensitive components and maintain process precision. During handling, cutting, and packaging, it covers sensitive areas to prevent scratches, contamination, and electrostatic damage. In high-temperature soldering processes, it protects components while preventing surface electrostatic buildup that could cause device failure. It also secures wafers, chips, or tiny components, providing anti-static protection and reducing the risk of damage or errors during manual operations.
PTFE tape in the semiconductor industry relies on its exceptional chemical inertness, high-temperature resistance, and low friction properties. It is widely used for protection, masking, securing, and precision processing. The low friction surface of PTFE is often used for demolding, separation, or sliding guidance in high-precision processes. During automated production or testing, it is used to secure wafers or chips, reducing friction and damage. It is also suitable for high-temperature processes such as curing, reflow soldering, and baking, protecting components from thermal damage.



