When faced with various high-temperature tapes, how should engineers make decisions? The key to selecting high-temperature tapes lies in the base material, as different materials directly determine their performance limits and application scenarios. PP (Polypropylene) based tapes can withstand temperatures of about 80-100°C, are the most cost-effective, and are commonly used for lightweight packaging, labels, and other room-to-medium temperature applications, making them an economical choice. PET (Polyester) based tapes can endure temperatures of 130-150°C, offering good insulation, mechanical strength, and cost advantages. They are the best value option for motor insulation, lithium battery production, and general high-temperature masking. When both temperature and reliability requirements are extremely strict, PI (Polyimide) based tapes should be chosen. With long-term temperature resistance exceeding 260°C, excellent dimensional stability, and flame retardancy, they are the top choice for PCB soldering, flexible circuits, and aerospace applications. For applications that need to remain stable in high heat, high humidity, or chemically corrosive environments, PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) based tapes are the ideal solution. They perform well in humidity and heat resistance as well as solvent resistance, making them especially suitable for multiple reflow soldering processes and insulation fixation in harsh conditions.

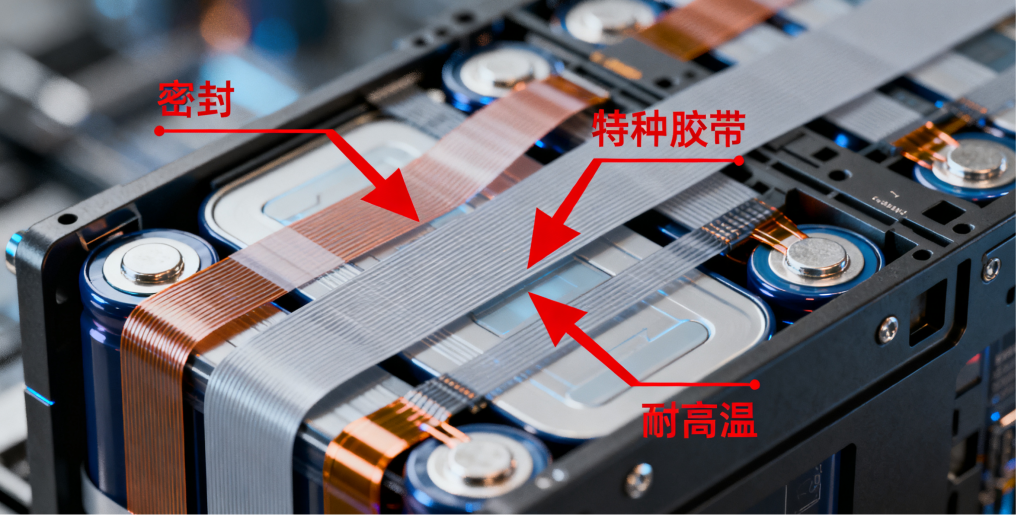
When selecting high-temperature tapes for the capacitor, semiconductor, and new energy industries, precisely matching the industry’s core standards is crucial to success. In the capacitor field, the focus must be on ‘insulation reliability.’ Thin, high-breakdown voltage PET or PI-based tapes should be the first choice, while products containing plasticizers must be strictly avoided to prevent dielectric contamination. Additionally, the temperature resistance should consistently exceed the operating limit of 105-125°C. Semiconductor processes have stringent requirements for ‘ultra-high cleanliness,’ necessitating the use of silicone-free, low-outgassing PI-based or specialized UV-reduced tack tapes to meet wafer-level particulate control and zero-residue standards, as any ordinary industrial tape would directly result in a significant yield drop. In the new energy sector, ‘safety tolerance’ is the primary principle. Lithium batteries require flame-retardant PI- and TPU-based tapes to resist electrolyte corrosion and impact vibrations, while photovoltaic modules must use UV-aging-resistant EPDM-modified PET tapes to ensure 25 years of outdoor durability.
Here are three steps to quickly lock in the target: First, set the temperature, clarifying long-term and short-term peak temperature resistance and allowing a safety margin; second, choose the substrate, selecting PI, PPS, PET, or other types based on core requirements like insulation, heat and moisture resistance, and cost; third, verify the details, confirming adhesion, insulation, and process compatibility, and when necessary, conduct sample tests to ensure absolute reliability. Following this process allows you to efficiently select high-temperature tapes that meet requirements while being economical and reliable.