What are polymer macromolecules?
On a macroscopic level, polymer macromolecules are large molecular chains formed by many simple molecules connected through chemical bonds, constituting the plastics, rubbers, and fibers we encounter in daily life. Polymer products include polyurethane, acrylates, silicones, and epoxy resins, each possessing unique functional properties such as high elasticity, weather resistance, heat resistance, and high strength. They are the cornerstone of modern industry and the source of innovation and applications for Zhejiang Ruibai New Materials Co., Ltd.
Understanding the macroscopic characteristics of polymers naturally raises the question: how can these properties be transformed into engineering materials that solve practical problems? Adhesive tape is a typical example of maximizing the value of polymer macromolecules. An ideal tape requires at least three layers: an adhesive layer that provides stickiness, a backing layer that bears strength, and a release layer for user convenience.
Depending on the backing material, industrial tapes are commonly classified into several major categories, each corresponding to different application scenarios:
PP (Polypropylene) Backed Tape
This is the most common general-purpose tape, mainly used for large-scale carton sealing and temporary protection of product surfaces (such as appliance panels and stainless steel plates). It is characterized by low cost, light weight, and good resistance to acids and alkalis, making it suitable for conventional applications with moderate performance requirements.

PET (Polyester) Tape
PET tape strikes a good balance between performance and cost. It has high mechanical strength, excellent electrical insulation, and good heat resistance (usually long-term heat resistance of 130°C to 150°C). Therefore, it is widely used for interlayer insulation and bundling of components such as motors, transformers, and inductors, as well as for protecting specific areas during PCB wave soldering and surface protection during metal stamping and stretching processes.

PI (Polyimide) Tape
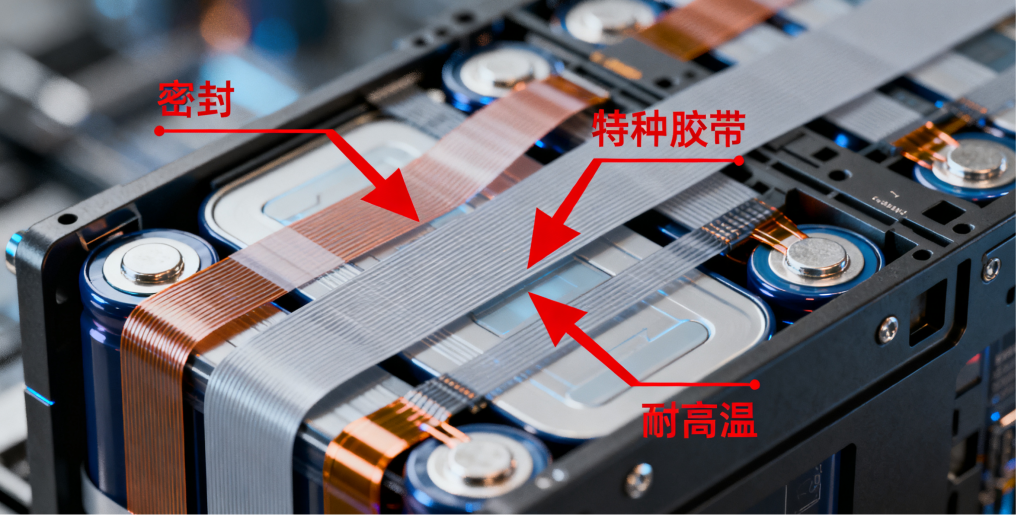
PI tape is an essential material in high-end electronics manufacturing and extreme environments. Its most notable feature is its excellent long-term high-temperature resistance (capable of withstanding temperatures above 260°C for extended periods and peak temperatures above 400°C for short periods), along with outstanding electrical insulation, flame retardancy, and dimensional stability. Its classic applications include: PCB soldering protection: protecting gold fingers and surrounding circuits during reflow soldering and wave soldering processes. Flexible printed circuit (FPC) reinforcement: applied to specific areas of the FPC to increase local strength and flexural durability. High-temperature motor/transformer insulation: used for slot insulation and phase insulation in motors with H-class or higher heat resistance ratings. Aerospace and automotive electronics: used for wire harness bundling, electrical insulation, and fixation in high-temperature areas.

PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) Based Tape
PPS-based tape is another type of top-tier high-performance tape. It competes with PI tape in certain areas (such as FPC reinforcement), but its characteristics include unparalleled dimensional stability and superior resistance to chemical solvents in high-temperature and high-humidity environments. Its main applications are: Reinforcement of high-frequency flexible printed circuits (FPCs): especially in cases where multiple reflow soldering processes are required and extremely high dimensional accuracy is crucial. Motor insulation in extreme environments: used in chemical environments with higher corrosion resistance requirements or in compressors resistant to refrigerants.

OPS (Oriented Polystyrene) Tape
This tape is mainly aimed at the consumer sector and is characterized by its extremely high transparency, gloss, and stiffness, as well as being very easy to tear by hand. It is almost exclusively used for packaging and sealing gifts and premium products, as well as stationery items like creative goods and planners, meeting the needs for both aesthetics and convenience.

TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) Based Tape
TPU substrates provide tapes with excellent flexibility, wear resistance, high elasticity, and oil resistance. They are mainly made into high-performance double-sided tapes to address stress and deformation issues in material bonding. Typical applications include: Automotive interior bonding: Securely bonding interior components of different materials, such as dashboards, door panels, and soundproof mats, to the vehicle body, while withstanding temperature changes and long-term vibrations inside the car. Composite material bonding: Reliably bonding different materials such as plastics, metals, and fiberglass. Footwear and textiles: Used for bonding shoe upper materials that require frequent bending and for attaching clothing labels.