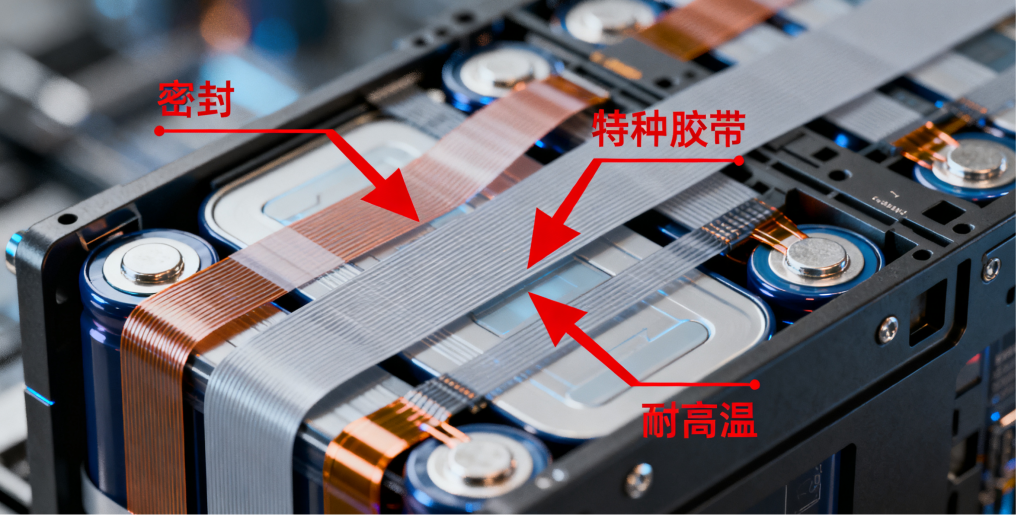
Adhesive tape in the lithium battery industry: an indispensable force for “adhesion” and “protection” – from small components to a major role.
From Small Component to Major Role
In the highly integrated product of lithium batteries, adhesive tape, seemingly an ordinary auxiliary material, actually plays multiple crucial roles. It is not merely a simple “adhesive,” but a core functional component that achieves electrical insulation, thermal management, structural fixation, and safety protection of the battery. Its performance directly affects the energy density, cycle life, safety, and production efficiency of lithium batteries.


Core Functions and Requirements of Lithium-ion Battery Tape:
- Excellent Electrical Insulation: Preventing short circuits between the positive and negative electrodes, and between the battery cell and the casing. This is the most basic and crucial requirement.
- Superior High-Temperature Resistance and Heat Resistance: Lithium-ion batteries generate heat during operation and charging. The tape must maintain stable performance at high temperatures (typically 80°C to 150°C, or even higher), without melting or shrinking.
- Stable Chemical Inertness: It must resist corrosion, penetration, and swelling from the electrolyte (usually organic solvents and lithium salts), maintaining its adhesion and strength over the long term.
- Good Mechanical Properties and Abrasion Resistance: During cell winding/stacking and assembly, it must withstand tension, friction, and compression to prevent breakage leading to insulation failure.
- Low Volatility and Non-Corrosiveness: It must not generate volatile gases in the vacuum environment inside the battery, and the adhesive must not corrode the battery cell materials. 6. Ultra-thin and consistent thickness: In today’s pursuit of higher energy density, the thickness of the tape is usually at the micrometer level, and the thickness must be uniform to avoid affecting the internal space and structure of the battery cell.
Main types of adhesive tapes and their applications in lithium battery manufacturing
Based on their application and function, lithium battery tapes are mainly classified into the following categories:
- Internal Cell Tape
This is the most technically demanding part, directly contacting the active materials and electrolyte.
- Tab Tape
- Function: Fixes and insulates the tabs (the positive and negative terminals of the battery), preventing short circuits between the tabs and adjacent electrodes or the casing.
- Requirements: Extremely high insulation strength, excellent electrolyte resistance, and strong adhesion.
- Common Materials: Black polyimide tape is the mainstream choice due to its high temperature resistance, good insulation, high strength, and puncture resistance. PET tape is also used.
- Winding/Lamination Tape
- Function: Fixes the ends of the electrodes and separators during the winding or lamination process, preventing them from loosening.
- Requirements: Moderate adhesion (firm enough to bond without affecting subsequent unwinding), ultra-thin thickness, and electrolyte resistance. • Common Materials: Acrylic adhesive PET tape is widely used.
- Termination Tape
- Function: Applied to the end of the battery cell winding, it provides additional insulation and protection, enhancing structural integrity.
• Requirements: Similar to winding tape, but with higher requirements for insulation and pressure resistance.
- Battery cell exterior and module assembly tape. This part of the tape focuses on structural fixation, insulation, and thermal management.

- Insulating Covering Tape
- Function: Wraps around the battery cell, acting as a second insulating barrier between the cell and the aluminum-plastic film (for pouch cells) or steel/aluminum casing (for cylindrical/prismatic cells).
- Common Materials: PET tape, PP tape; polyimide tape is used in some high-requirement applications.
- Fixing Tape
- Function: Fixes multiple battery cells into a battery module, securing protection boards, wiring harnesses, sampling lines, etc.
- Requirements: High adhesion, good initial tack, sufficient thickness, and cushioning.
- Common Materials: Foam tape (such as acrylic foam) is preferred due to its excellent cushioning, shock absorption, and sealing properties, and its ability to fill gaps between components. VHB tape is also commonly used for high-strength structural bonding.
- Thermally Conductive Tape
- Function: Conducts heat from the battery cell or module to the heat sink or cooling system, while also providing adhesive bonding.
- Principle: Filling the adhesive or substrate with ceramic powders such as alumina and boron nitride, which have high thermal conductivity.
- Common Forms: Thermally conductive silicone cloth, thermally conductive tape, etc.
- Marking and Protective Tape
- Function: Used for affixing QR codes and barcodes to batteries, or to protect the battery surface from scratches during production.
• Common Materials: Easy-tear masking tape, PET label tape, etc.
Industry Trends and Future Challenges
- Ultra-thin and lightweight: To improve energy density, tapes are evolving towards thinner (e.g., 8μm, even 5μm) and stronger materials.
- Functional integration: Single tapes are trending towards multiple functions, such as insulation + thermal conductivity, fixation + cushioning, insulation + flame retardancy, etc.
- New material exploration: Developing new high-temperature resistant polymer substrates with lower costs than polyimide (PI) but similar performance, such as aramid and PEEK.
- High-speed automated adaptation: Tapes need better unwinding force and stability to adapt to high-speed production lines producing dozens of cells per minute, avoiding tape breakage and misalignment.
- Ultimate safety and reliability: Studying the behavior of tapes under thermal runaway conditions to develop flame-retardant or even heat-insulating tapes that can slow the spread of fire.
—
In the intricate and complex internal world of lithium batteries, tapes, though small, are the unsung heroes ensuring their safe, reliable, and efficient operation. From precise insulation positioning within the battery cell to robust structural bonding and efficient thermal management at the module level, the application of adhesive tape is ubiquitous. As lithium battery technology continues to evolve towards higher energy density, faster charging speeds, and greater safety, the demand for high-performance, multi-functional specialty adhesive tapes will become increasingly urgent, which will continue to drive innovation and progress in adhesive tape material science and process technology.